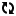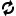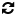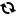Bollinger Bands is a popular technical analysis tool that was developed by John Bollinger. It consists of a set of three lines plotted on a price chart and is widely used by traders in the forex trading industry to analyze price volatility and identify potential trading opportunities. In this article, we will explore how to use Bollinger Bands effectively and leverage their insights in forex trading.
1. Understanding the Components of Bollinger Bands:
Bollinger Bands consist of three lines: the middle band, the upper band, and the lower band. The middle band is a simple moving average (SMA) of the price over a specific period, typically 20 periods. The upper and lower bands are calculated by adding and subtracting a certain number of standard deviations from the middle band. The standard deviation value is often set to 2, which means that the upper and lower bands will encompass approximately 95% of price data within that range.
2. Volatility Analysis:
One of the primary uses of Bollinger Bands is to measure price volatility. When the price is experiencing high volatility, the distance between the upper and lower bands expands, indicating wider price swings. Conversely, during periods of low volatility, the bands contract, suggesting a potential consolidation or range-bound market. Traders can use Bollinger Bands to assess market conditions and adjust their trading strategies accordingly. For example, in high volatility environments, traders may consider employing breakout strategies, while in low volatility periods, range trading strategies might be more suitable.
3. Overbought and Oversold Conditions:
Bollinger Bands can also help identify overbought and oversold conditions in the market. When the price approaches the upper band, it suggests that the market may be overbought, indicating a potential reversal or a pause in the uptrend. Conversely, when the price nears the lower band, it indicates oversold conditions, implying a potential reversal or a pause in the downtrend. Traders can use these signals in conjunction with other technical indicators or price patterns to make informed trading decisions.
4. Bollinger Squeeze:
The Bollinger Squeeze is a powerful pattern that traders often watch for. It occurs when the bands contract significantly, indicating a period of low volatility. This compression is usually followed by a significant price move, characterized by a breakout or a strong trend. Traders can take advantage of the Bollinger Squeeze by placing pending orders above the upper band and below the lower band, anticipating a potential price breakout. It's important to exercise caution and wait for confirmation signals before entering trades based on the Bollinger Squeeze.
5. Confirmation with Other Indicators:
While Bollinger Bands can be used as a standalone tool, incorporating other technical indicators can enhance the accuracy of trading signals. Traders often combine Bollinger Bands with oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or the Stochastic Oscillator to confirm overbought or oversold conditions. When the price touches or exceeds the upper band while the oscillator is in the overbought territory, it strengthens the bearish signal. Conversely, when the price touches or falls below the lower band while the oscillator is in the oversold territory, it reinforces the bullish signal.
6. Trend Identification:
Bollinger Bands can also assist in identifying the direction of the trend. When the price consistently trades near the upper band and the bands are sloping upward, it indicates a strong uptrend. Conversely, when the price consistently trades near the lower band and the bands are sloping downward, it suggests a strong downtrend. Traders can use this information to align their trades with the prevailing trend or look for potential trend reversals when the price starts trading outside the bands.